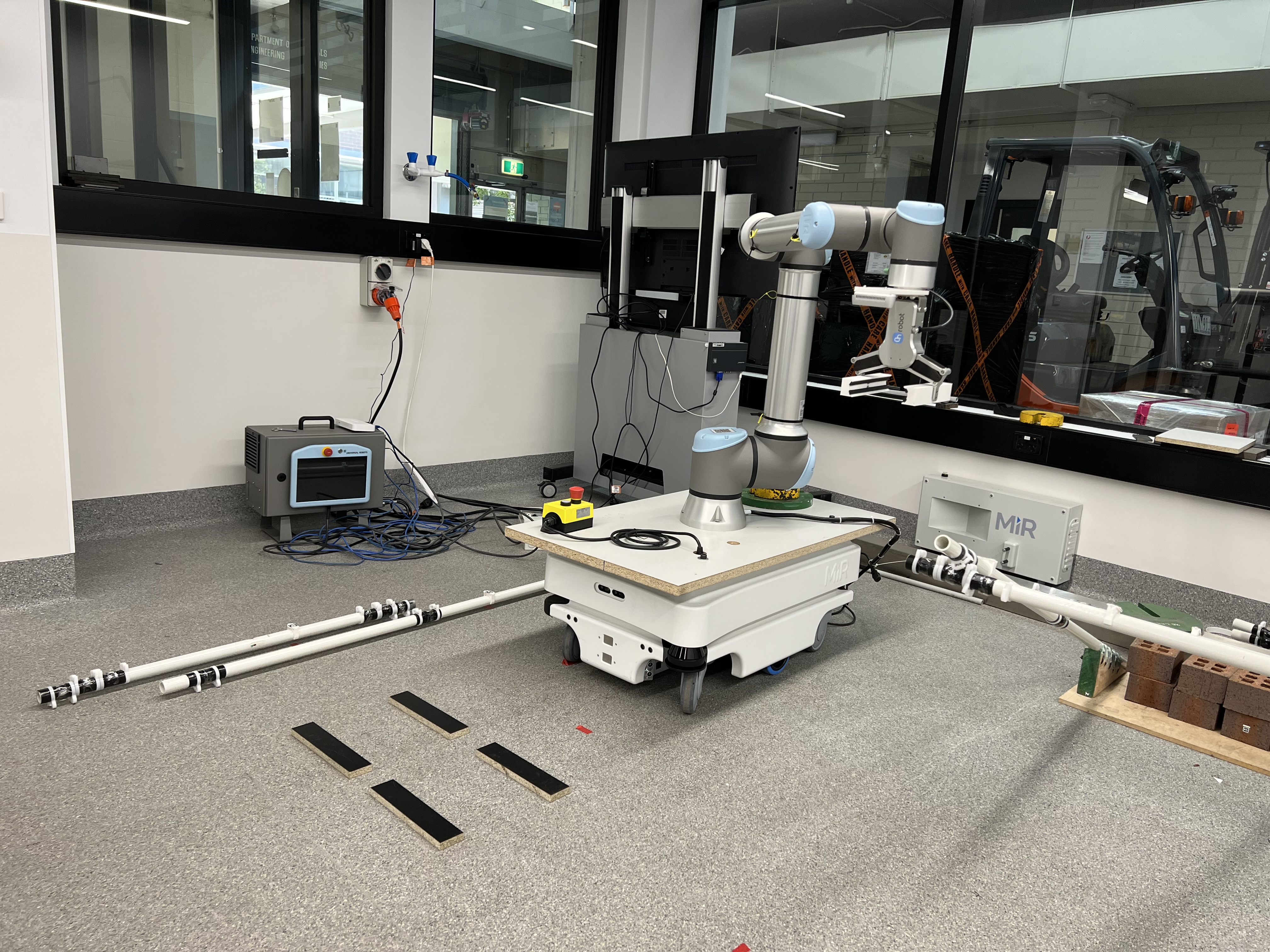
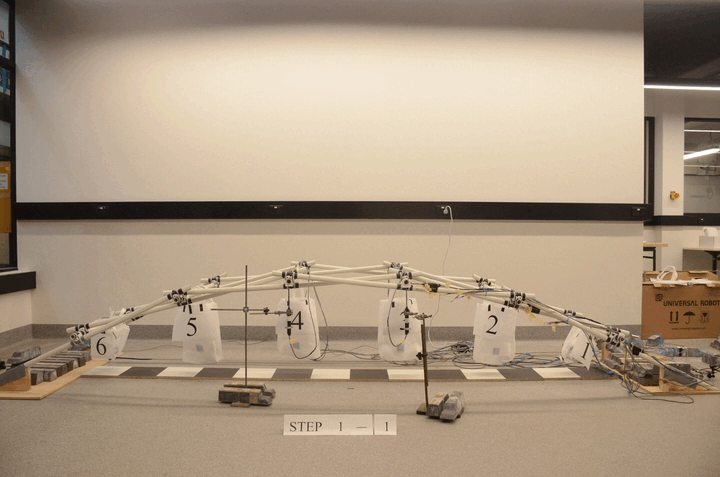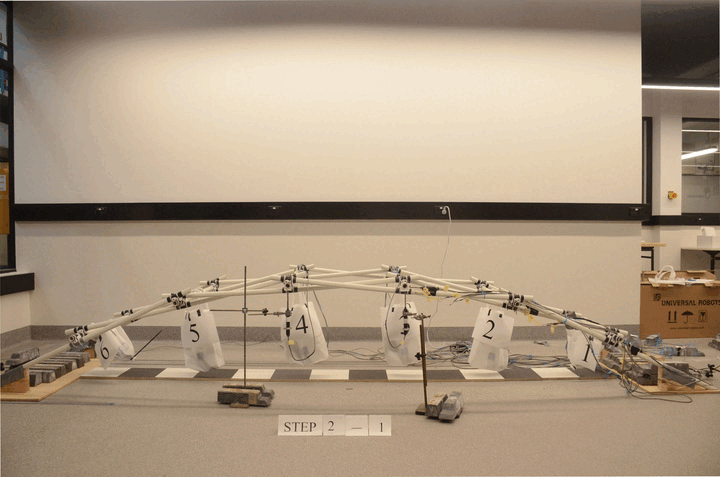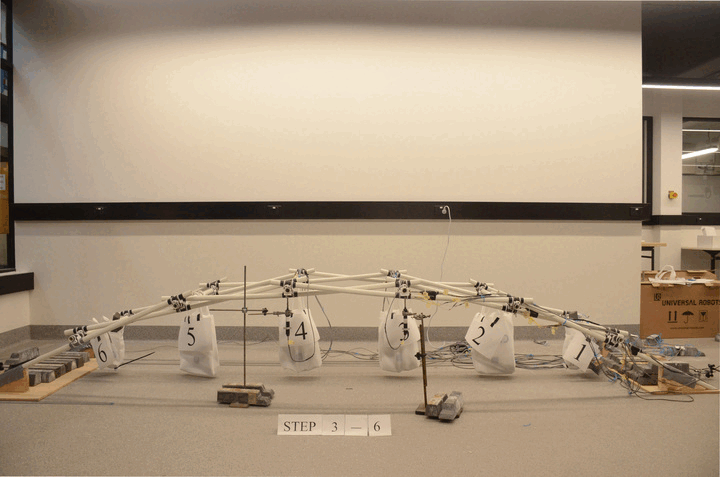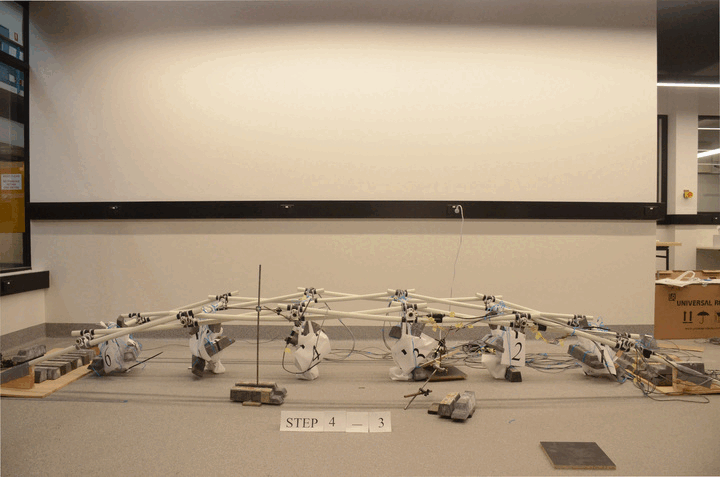
Robotic construction of reciprocal frame (RF) structure
"In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the interest on robotics across various industries, including medical surgery, manufacturing, agriculture, military, transportation, and construction. Robotic technologies have also shown great potential for applications in construction industry to improve efficiency, precision and safety, particularly in consideration of the repetitive, low-skill, and sometimes high-risk nature of many construction tasks. These advantages may also make robotic technologies more cost-effective and reliable than conventional construction methods in both short term and long run. The adoption of robotic technologies in construction is not only limited to efficiency improvements, it also holds the potential to significantly reduce construction waste and decrease the carbon footprint of this industry. As a result, robotic technologies may also contribute to the sustainable development of the construction industry, making them an increasingly attractive research interest for the construction industry."
(Chea et al., 2023)